8 Digital Transformation Technologies and Their Business Impact
What are Digital Transformation Technologies?
Digital transformation is the process of reshaping the company’s operations via the use of digital technologies to increase productivity, boost engagement, and enhance user experience. Digital transformation may entail developing a digital version of already-existing products or services, improving the operational effectiveness of already-existing companies, or even developing entirely new products and services that were unthinkable before the advent of the internet. There is more to digital transformation than just technology. Changes in organizational culture and business procedures are equally crucial to the organization’s success. Large, successful enterprises may compete with the more nimble, digital-only competition with digital transformation initiatives, while smaller businesses can adapt their product offerings to a changing market.

The digital transformation does not revolve around a particular technology. Any technology that enables a business to develop and produce better results can be included. We’ll discuss some cutting-edge technologies frequently employed in digital transformation initiatives—most initiatives use multiple of these technologies.
Organizational Digital Transformation
Although new technologies are essential to the digital transformation, they cannot function independently. Any organization going through a digital transformation needs to think about how its organizational culture, business models, and business processes will change.
Business processes transformation
In order to adapt to new corporate objectives, competition, and customer demands, existing processes and workflows must be modified. Business transformation is a subset of digital transformation, which assists an organization in creating a technical foundation that fosters growth and change.
Business Model Transformation
Business model transformation considers how value is produced in the sector and what new opportunities technology can create, whereas organization process transformation concentrates on the workflows and tasks carried out by the business in everyday operations. When a company model is transformed, it looks at new ways to serve the market to add value and boost performance.
Organizational and Cultural Transformation
In order for a digital transformation to be successful, it must be coordinated with the organization’s values and culture. It is crucial to gain employee support and foster trust in the company, its culture, and the digital endeavor. Lack of agreement regarding digital transformation may cause the adoption of new technology to be delayed or negative.
Top Digital Transformation Technologies

1. Cloud Computing Technology
The supply of computing services in a flexible and scalable manner, frequently but only sometimes using outside providers, is called cloud computing. Services offered by cloud computing can be divided into three groups:
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
This category provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
This category provides a platform for developing, running, and managing applications and services without the need for managing the underlying infrastructure.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
This category provides access to software applications over the internet without needing installation or maintenance on the customer’s end. Examples include email services, customer relationship management (CRM) systems, and project management tools.
Cloud Computing is one of the key digital transformation technologies as it offers agility, scalability, and flexibility. Because traditional infrastructure is frequently insufficiently sophisticated, scalable, agile, and cost-effective to run the necessary digital infrastructure, the majority of digital transformation initiatives make use of Cloud Computing.
2. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
The goal of machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI/ML) is to simulate human cognitive processes. Expert systems, natural language processing, computer vision, predictive analytics, and speech recognition are some examples of specific artificial intelligence applications.
Digital Transformation initiatives heavily rely on AI/ML as part of new business strategies. These are essential Digital Transformation technologies for enhancing productivity as well as for making better use of the data that companies gather. Businesses may build creative ideas and better products and services by gaining actionable insights from data.
3. Big Data
Data is regarded as the pulse of the modern economy and is a valuable asset for the majority of enterprises. This has resulted in exponential expansion, which is both a challenge and an opportunity for any organization. This growth is only anticipated to continue in the upcoming years. Big data can contain structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data that was gathered by businesses as part of routine business operations, from customers, or from outside sources. Predictive modelling, data mining, and other sorts of data analytics can all be done with this data. Organizations may handle massive amounts of data, extract information pertinent to the business, develop strategic models, and make decision-based on data by applying big data analytics.
4. Real-Time Analytics
As soon as data enters the system, it is analysed in real-time using relevant resources. The ability to act on data in a fashion that users perceive as instantaneous is referred to as “real-time.” Real-time data delivery from operational systems is made possible by streaming data architectures, which also make use of powerful analytics engines and facilitate quick operational decisions. Robotic process automation (RPA) and other types of automated policy enforcement can execute these choices and hence Real Time Analytics is a major Digital Transformation technology.
5. Internet of Things and 5G
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of computers, machines, and other items that can communicate with one another and share data. They frequently have the ability to operate without supervision from a person or a traditional computer system. The Internet of Things requires more bandwidth, faster transmission speeds, and flawless connections, which 5G technology can provide. For instance, as part of their digital transformation, the majority of the world’s big cities have set up a network of IoT sensors, many of which are connected by 5G. Digital transformation in the manufacturing sector is being driven by the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), often known as Industry 4.0. With the use of this technology, organizations may enhance workflows and boost flexibility, innovation, speed, and quality.
IoT plays a key role in enhancing customer satisfaction in the retail sector by offering insightful data on how customers buy and use products. Wearable technology and portable medical equipment that may be used in patients’ homes or physically attached to them make telemedicine possible in the healthcare industry.
6. Augmented Reality
Digital information is connected to a visual user experience using augmented reality (AR). Instead of creating a fully manufactured environment like virtual reality does, augmented reality uses an existing environment and adds new information on top of it.
A company can use AR for both employee tasks and consumer interactions. The system increases productivity, facilitates knowledge transfer, improves training, and provides superior customer service. With it, technology will be more intuitively used, and we will interact with digital systems differently.
7. Digital Twin
A digital twin is a technology that connects the digital and physical worlds. Virtual representations of physical objects are called digital twins.
The real object has a number of sensors connected to significant functional regions. These sensors produce data on a range of performance metrics for an object, including energy output, temperature, and environmental variables. After that, a processing system receives the data and applies it to the digital copy.
As a result, businesses can utilize the virtual model to run simulations, look into performance problems, and even make adjustments. The goal is to provide insightful discoveries that can be applied to the actual physical thing.
Applications of digital twins include:
- Industrial Equipment Monitoring: Monitoring the performance and condition of industrial equipment in real-time to predict and prevent failures.
- Smart Buildings: Creating virtual models of buildings to optimize their design, energy consumption, and maintenance.
- Healthcare: Digital twins in healthcare can help simulate and analyze patient-specific data to improve patient outcomes.
- Supply Chain Management: Optimizing supply chain operations by creating virtual models of the entire supply chain to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks.
- Urban Planning: Creating virtual models of cities to simulate and analyze different scenarios to improve urban planning and decision-making.
- Automotive: Digital twins can be used in the automotive industry to simulate and test the design, performance, and reliability of vehicles before they are manufactured.
8. Additive Manufacturing and 3D Printing
Additive Manufacturing (AM) and 3D Printing are key digital transformation technologies that allow the creation of physical objects by building them up layer by layer, rather than by subtracting material as in traditional manufacturing processes. This enables greater design freedom, reduced waste, and faster production times.
3D Printing has a wide range of applications, from prototyping and product design to the creation of end-use parts in industries such as aerospace, healthcare, and consumer goods. The use of AM and 3D Printing is growing rapidly due to advances in materials, software, and hardware, making it possible to produce complex and high-performance parts.
By combining digital design and production processes, AM and 3D Printing are transforming traditional manufacturing methods and enabling new business models, such as on-demand production and local or decentralized production. This technology is also contributing to the Fourth Industrial Revolution by enabling the development of the Internet of Things (IoT), Industry 4.0, and the integration of digital and physical systems.
Cloud Computing – The First Step Towards Digital Transformation
Cloud computing is the key element of digital transformation, elevating it beyond the adoption stage and incorporating the tools, rebuilding process, and experience of a virtual environment. An organization must implement a cloud-first or hybrid cloud management strategy if it wants to accomplish its objectives and ensure its long-term viability.
ESDS’ eNlight Cloud is a cloud transformation solution that leverages the power of cloud computing to help organizations move their IT infrastructure to the Cloud. The solution is built on a scalable, secure, and high-performance cloud platform that supports various Enterprise Storage Devices (ESDs).
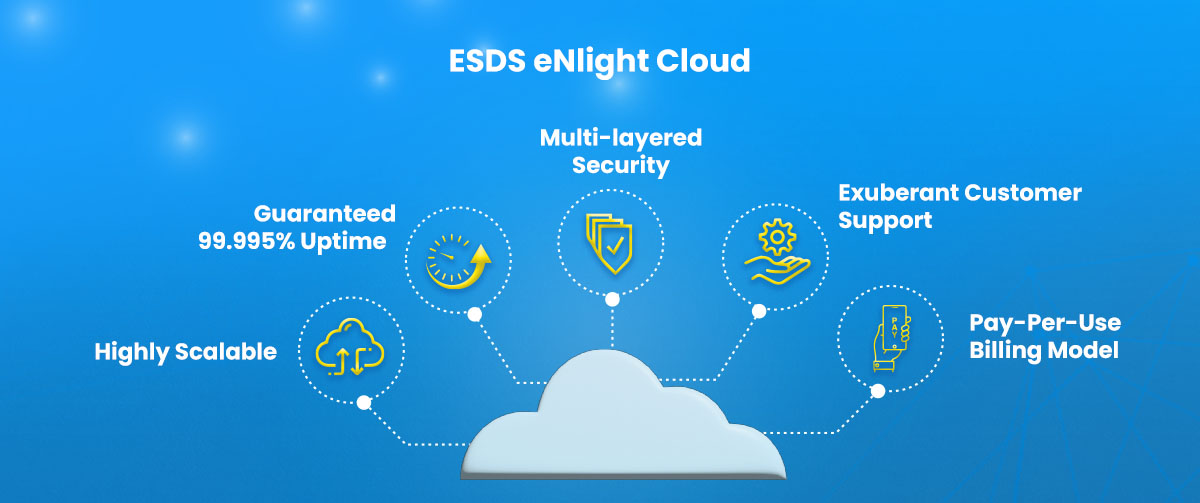
By utilizing cloud computing, eNlight Cloud enables organizations to access the resources they need, when they need them, with the flexibility and scalability to meet the demands of their business. This results in reduced IT costs, improved operational efficiency, and increased business agility.
eNlight Cloud also supports various deployment models, including public, private, and hybrid clouds, allowing organizations to choose the deployment model that best suits their needs. The platform also offers a range of security features, such as encryption, data protection, and access control, to ensure the protection of sensitive data.
Overall, eNlight Cloud is a powerful cloud transformation solution that helps organizations modernize their IT infrastructure, increase efficiency, and improve their overall competitiveness in the digital economy.
- Top 5 Data Center Trends for 2024 - October 11, 2023
- Top 15 Cloud Computing Trends 2024 - October 4, 2023
- What is Infrastructure Monitoring and Why Infrastructure Monitoring Tool is Important for Your Business? - September 20, 2023
