VoIP: Understanding Architecture and Features
VoIP or Voice over Internet Protocol represents a technology used for voice conversations with an Internet Network or Internet Protocol. It transmits the voice signals in the digital form in the packets and then sends it across the digital form in analog circuits through a mobile phone company or a conventional PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network). These protocols are used for sending voice signals over an IP network protocol known as IP protocol. Voice over IP can occur through any IP network, including the ones connected to the Internet like local area networks (LANs).
Differences Between VoIP and IP Telephony
The following are some differences between VoIP and IP Telephony
VoIP
- It is a technology used to make a voice routed over a data network such as the public Internet.
- With VoIP, a PBX (Private Branch Exchange) is used for distributing the calls within an organization. However, it is important to note that PBX must support the Internet protocol that is being used.
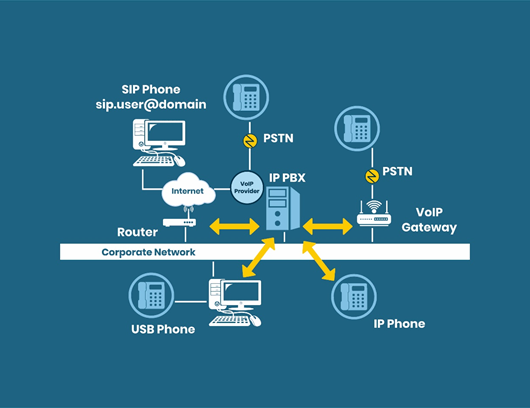
IP Telephony
- IP telephony is built on the capabilities of a VoIP. It comprises several additional software-based features that run on computers for replacing the existing infrastructure of the PSTN.
- IP phones, also known as SIP or softphones designed especially for VoIP, are connected to a data network rather than a phone network.
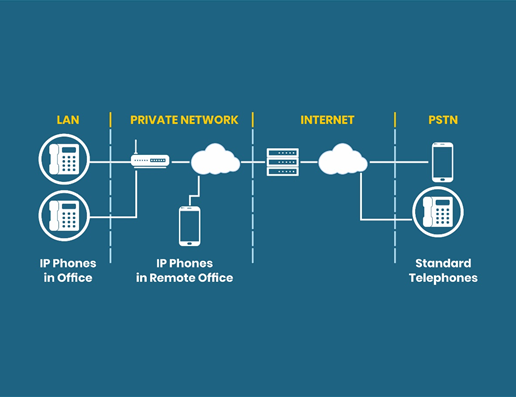
History of VoIP
The first technology for telephony over the Internet was presented in February 1995 by VocalTec. The proposed Internet phone can be considered in the primitive stage compared to the technology available today. The software was designed to run on a computer with 33,486 MHz processors or higher. The user would talk with another user using a modem to the computer’s microphones and speakers. In the transferring processing, the software transforms, or compressed voice was spoken over the microphone. Next, the compressed voice would be transported over an IP packet data format as a standard Internet session. However, using this technology, the conversation remains limited between two computer users (PC to PC).
A year later, in March 1996, VocalTec announced that it would work with other companies for producing hardware known as the Voice Gateway. Voice Gateway would enable audio connections between a phone and an Internet phone using the Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN). There was still a challenge in addressing and reaching a user on a computer present anywhere in the world. The end-user must know the remotely-located computer’s IP address, and it was not easy to find it if there was no previous communication. Voice Gateway looks for another one that stores the telephone number of user searches. Telephone numbers are considered to be much easier than IP addresses. Thus, the functionality of Voice Gateway dealt simultaneously with the barriers to grid connection and addressing.
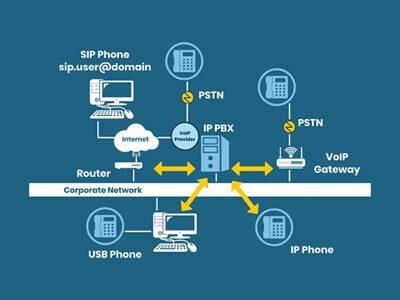
Working of VoIP
VoIP is a technique for converting voice signals into digital data and then transmitting it on the Internet using the TCP/IP protocol. VoIP wraps the data packets before transmitting across the Internet. With VoIP, users can make a call over the world using an active Internet connection using Wi-Fi instead of your service provider’s network.
VoIP Protocols
Some of the commonly used VoIP Protocols used today include- Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) and H.323. These protocols are widely known as Intelligent-End Protocols. They contain the ‘intelligence’ required to find and set up a connection between the user the device (local host) and the device user will call (remote device).
1. Session Initiation Protocol (SIP)
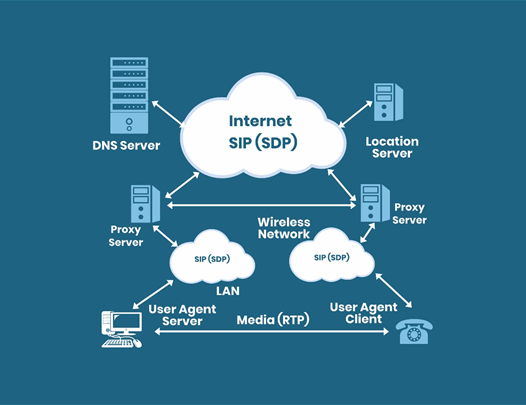
SIP refers to a common Internet protocol that works by interchanging the short lines of ASCII text. It is highly modular, simpler, and flexible. It can be easily integrated with other Internet protocols. However, it doesn’t collaborate with any of the existing telephone system signaling protocols.
Components of Session Initiation Protocol
Following are the two major components included in the SIP protocol
- User-Agent
User-Agent is present at SIP end stations and includes a User Agent Client (UAC) and User Agent Server (UAS). The User-Agent Client issues the SIP requests, whereas the User-Agent Server responds to each SIP request.
- Network Server
In a SIP protocol, there are three major types of servers, namely- redirect server, proxy server and registrar.
2. H.323
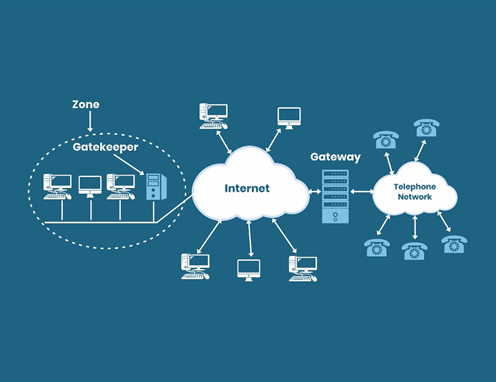
H.323 refers to a telephone industry standard that describes the complete protocol stack. This standard also defines what is permitted and what is prohibited. The systematically-defined protocols help ease interoperability; however, it is complex, making it difficult for the next-generation applications to adapt it.
Components of H.323 Protocol
Following are the major components present in the H.323 protocol
- Terminal
A terminal serves as the endpoints inside an IP network. Terminals provide signaling and control, along with two-way communication in real-time and codecs. Codecs are defined as a device or computer program that encodes or decodes digital data or signals.
- Gateways
Gateways refer to a connection path that is made between the packet-switched network and the circuit-switched network. A gateway can be removed if there no other networks are connected.
- Gatekeepers
A gatekeeper’s important functionalities include translation of addresses, controlling bandwidth, zone management, and managing the admissions. However, gatekeepers’ core functionality is to regulate the endpoints present within its rule, also known as Zones.
Advantages of VoIP
Following are the key advantages of using a VoIP
- Savings in Costs
By using VoIP, the user needs to pay for his Internet connection. Calls taking place between individuals having VoIP equipment, even on international calls, are free of cost.
- Rich in Features
VoIP provides an array of features such as call forwarding, blocking. Automatic call distribution and interactive voice recognition.
- Supports Multitasking
Besides making the traditional phone calls, VoIP can also be used for sending documents, images, and videos simultaneously. This allows businesses to seamlessly integrate meetings with their employees or clients spread across the globe.
- Enhanced Security
VoIP can be used for mitigating various security threats through advancements made in IP technology like encryption and better identity management.
VoIP in Indian Scenario
VoIP calling apps such as WhatsApp and Skype have emerged and had already started giving tough competition to the traditional PSTN-based voice technologies. VoIP has several benefits over PSTN calling, and thus, they are becoming a preferred option for business calls.
Talking particularly about the Indian scenario, the Internet Service Providers or ISPs are forbidden to connect with PSTN/PLMN networks under the TRAI guidelines. Hence, IP-based VoIP calls can’t be mixed with PSTN calls.
What’s Allowed?
- VoIP to VoIP Calls in India
Calls starting on a VoIP device and terminating on a VoIP-enabled device
- Inbound International VoIP Calls
International calls don’t fall under the ‘boundaries’ of TRAI. International inbound calls that terminate in VoIP devices in India are allowed. One can start a VoIP-based international inbound calling center in India
- International Outbound Calls
International VoIP outbound calls starting in India are legal; thus, one can start a VoIP-based international outgoing calling center in India
What’s Not Allowed?
- Calls from Traditional Telephone to VoIP Devices in India
Intermixing of VoIP and PSTN calls is not permitted and considered to be illegal in India
- Calls from VoIP Device to Traditional Landline / Mobile in India
This is also known as VoIP dial out and subsequently not allowed in India
- Considering Data Centers in India to Overcome Economic Conditions - May 10, 2022
- Determining Why Your Organization Needs Web Application Security - February 11, 2022
- How Does a Business Benefit with Managed Services - January 21, 2022
This is nice. We got good reference.
Very Informative!!! Thank You.
Thank you for article . I highly appreciated for you article. please give me some information to increase performance like as your website.
this is a very useful article.
This is extremely valuable information. This message will help more for new users. who is looking for VoIP Connection
This article is really a great discussion about VOIP Architecture And Features.
Thanks for sharing this.
Good post for VOIP. Thanks
good post thanks for the info