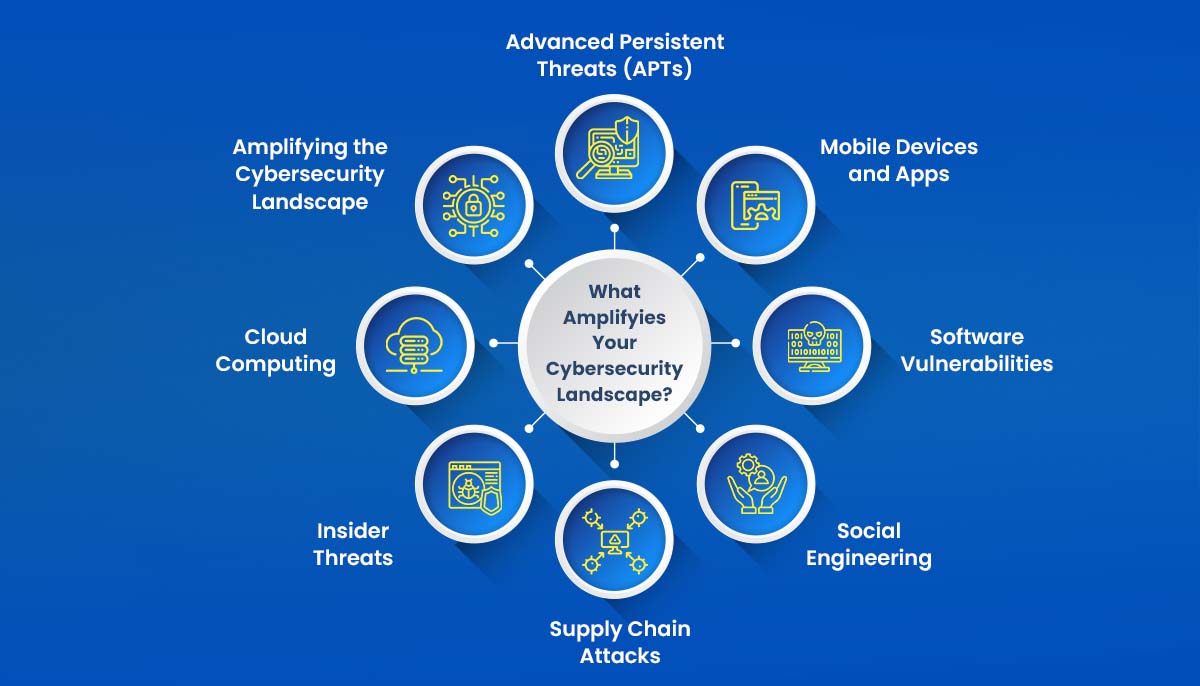
Understanding the Risks: 8 Factors Amplifying the Cybersecurity Landscape

By 2025, the annual cost of cybercrime for companies is projected to reach $10.5 trillion globally, a significant increase from the $3 trillion recorded in 2015.

In the vast, interconnected realm of the digital age, where the heartbeat of technology pulses ceaselessly, a burgeoning force looms with undeniable menace—the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape. As our world becomes increasingly reliant on technology, the once-unfathomable potential of cyberspace now presents an equally unprecedented range of threats. From shadowy hackers lurking in the shadows to insidious malware creeping through unseen cracks, the security of our digital assets hangs delicately in the balance.
As our reliance on digital systems and networks grows, so does the potential for cyber-attacks. Organizations and individuals must understand the factors contributing to the expanding cyber-attack surface. This article delves into eight key factors fueling the growth of vulnerabilities, posing significant risks to businesses and individuals.
1. Internet of Things (IoT) Devices
The rise of Internet of Things (IoT) devices has brought about tremendous convenience and new security challenges. IoT devices, ranging from smart appliances to wearables, often lack robust security measures, making them attractive targets for cybercriminals. As the number of connected devices increases, so does the potential attack surface, leaving organizations and individuals vulnerable to breaches. It is essential to prioritize security measures to safeguard IoT ecosystems.
2. Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses store and process data, enabling scalability and flexibility. However, it also presents new security considerations. While cloud service providers implement robust security measures, data breaches and unauthorized access to cloud-based resources remain a concern. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud technologies, it becomes crucial to implement stringent security measures and regularly assess and monitor the integrity of cloud environments.
3. Mobile Devices and Apps
The widespread use of mobile devices and applications has transformed how we connect and interact. However, it has also expanded the attack surface for cybercriminals. Malicious actors exploit mobile operating systems and app vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to personal and corporate data. With the growing reliance on smartphones and tablets, securing these devices against cyber threats becomes paramount. Regular updates, strong passwords, and awareness of potential risks are vital for mobile security.
4. Social Engineering
Social engineering remains one of cyber criminals’ most prevalent and effective techniques. These tactics manipulate human psychology to deceive individuals into divulging sensitive information or performing actions compromising security. Phishing emails, pretexting, and baiting are common social engineering techniques. Organizations must educate employees and users about these risks and implement robust security awareness programs to prevent falling victim to such attacks.
5. Software Vulnerabilities
Software vulnerabilities continue to be a major concern in the realm of cybersecurity. Cybercriminals exploit weaknesses in software code to gain unauthorized access, disrupt services, or steal sensitive data. Timely software updates and patches are essential to address these vulnerabilities and protect systems from exploitation. Employing automated vulnerability scanning tools and regular security audits can help effectively identify and mitigate software vulnerabilities.
6. Insider Threats
Insider threats refer to the risks posed by individuals within an organization who have authorized access but misuse their privileges. These individuals can include employees, contractors, or business partners. Insider threats can be intentional or unintentional, severely affecting an organization’s security posture. Implementing strict access controls, conducting background checks, and fostering a culture of security awareness is crucial to mitigating the risks associated with insider threats.
7. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs) are sophisticated and persistent cyber-attacks that target specific organizations or individuals over an extended period. These attacks often combine techniques, such as social engineering, zero-day exploits, and malware, to gain persistent access to a target’s network. Detecting and responding to APTs requires advanced threat intelligence, proactive monitoring, and robust incident response capabilities. Organizations must invest in advanced security technologies and skilled cybersecurity professionals to combat APTs effectively.
8. Supply Chain Attacks
Supply chain attacks have emerged as a significant concern in recent years, highlighting the vulnerabilities associated with interconnected business ecosystems. Cybercriminals target the weakest link in the supply chain to gain unauthorized access to systems or inject malicious code into software or hardware. Strengthening supply chain security through due diligence, security audits, and secure development practices is crucial to mitigating this risk. Organizations must vet their suppliers, implement strong access controls, and continuously monitor the supply chain’s integrity.
Conclusion:
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, cyber threats loom, and understanding the factors contributing to the expanding cyber-attack surface is paramount. By addressing the eight factors discussed in this article – IoT devices, cloud computing, mobile devices and apps, social engineering, software vulnerabilities, insider threats, APTs, and supply chain attacks – organizations can enhance their cybersecurity posture and protect themselves from potential breaches.

It is crucial to stay informed about the latest security trends, implement robust security measures, and foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness. By prioritizing cybersecurity and investing in the right resources, businesses and individuals can fortify their defenses, safeguard sensitive data, and navigate the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape.
Remember, cybersecurity is a continuous process requiring constant vigilance, proactive measures, and adaptation to emerging threats. Stay secure, stay vigilant!
- Decoding Generative AI: A Comprehensive Guide to Gartner’s Impact Radar - January 2, 2024
- 5 Best Practices for Cloud Security in 2024 - December 29, 2023
- 10 Best Machine Learning Ops Strategies for Cloud Environments in 2024 - December 29, 2023
