SAP ERP Client Server Architecture

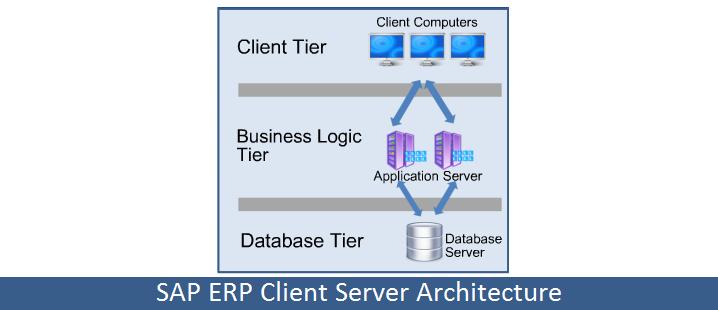
The SAP-ERP – (System Application Product – Enterprise Resource Planning) uses a three-tier client-server architecture, consisting of:
- Database server
- Application server
- Presentation layer on the client -side
With this structure, it is possible to distribute the tasks to other machines with increasing demands, thereby increasing the efficiency of the overall system.
Database
The various SAP ERP Hosting components set a custom relational SQL – database ahead, which is not supplied by the company itself. SAP ERP and the SAP Web Application Server support in addition to the in-house SAP MaxDB – common products such as DB2, Informix, Microsoft SQL Server and Oracle.
Application Servers
The entire business processing is done in the application server through special programs utilizing the proprietary programming language ABAP / 4 ( Advanced Business Application Programming Language are written) and through tools such as Data Dictionary, mask generator to supplement or Query Management.
The programs are executed within a specific runtime environment, which is called SAP “kernel”.
Kernel
The kernel is in C programming and can – in contrast to most of ABAP programs – will be viewed but not modified by the customer. The kernel abstracted from both the conditions of the operating systems used and of the special SQL – syntax of the used DBMS, so that ABAP programs on all platforms are capable of running for ABAP kernel.
The kernel contains the following essential components:
- Lock server
- Update processes
- Spooling
- Dialog processing
- Background Processing
The processes can be distributed as needed depending on different machines. The simplest case (all processes running on an application server) is referred to as so-called “central instance”. For smaller scenarios, this arrangement is sufficient, and often can be maintained and the database on the same machine. Some components (especially locking and update processes) may exist only once per system, the “workhorses”, however (the dialogue and background processes), which perform the actual program execution can be distributed across multiple machines. The combination of database and application server processes is called ERP system.
Customizing
Unlike most of the smaller ERP systems, numerous variations of the functionality can be set only by parameters in SAP ERP. The adjustments to these settings are as customizing designated and must be performed for each implementation of the system or module.
The plurality of parameters is controlled by means of several thousands of database tables, which are evaluated at run time. Your care is via a tree parameter, which is constructed similar to the application structure for modules and Care Masks and function information for the permissible entries offers.
Alternatively, this can also be done directly on the care of the control tables.
Are the settings through the existing customizing functions no longer represent the standard programs in a number of places extension points available, where via a defined interface customized program parts can be embedded in the standard processing ( User Exits, Customer Exits, Business Add-Ins (BAdI), enhancements).
If these options are not enough, (almost) all standard programs can be modified as per customer specifications. These “modifications” are recorded automatically in order to assign responsibility in case of errors can. Because of the increased sequence expense (balance during the update of the standard programs) modifications are, however, avoided if possible.
The interplay of the various parameters is only partially documented – adaptation to a company therefore needed on the part of the responsible consultant a certain experience.
Resources:
- How Cloud Computing Is Changing The Labor Market - March 25, 2015
- Adopting Infrastructure as a Service Can be a Good Deal - March 17, 2015
- Will Virtualize? Take These Six Points Into Consideration - March 12, 2015