What is the Difference Between Data Sovereignty and Data Residency?
TL;DR (Quick Summary) – Data sovereignty defines which country’s laws govern your data, while data residency defines where the data is physically stored. In India, multiple laws like the DPDP Act, IT Act, and TRAI rules create a complex compliance environment. ESDS Sovereign Cloud helps enterprises stay fully compliant by keeping data within Indian jurisdiction and ensuring secure, locally governed cloud operations.
Data sovereignty and data residency are critical pillars of modern data management, defining how organizations gather, store, and utilize personal information, particularly in cloud environments where data often crosses borders. The physical location of cloud servers determine data residency, while sovereignty dictates which nation’s laws govern that data. Understanding the distinction between the two is essential for any enterprise operating in a digital ecosystem.
In India, these concepts intersect with one of the most intricate legal frameworks for data privacy. With nearly five key laws spanning various sectors, organizations often find themselves navigating overlapping and evolving compliance requirements.
For instance, the IT industry follows two separate regulations, whereas telecom companies must adhere to guidelines from the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI). The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, further extends to all businesses that collect, process, or share personal data of Indian citizens. Meanwhile, the upcoming National E-Commerce Policy is expected to add another layer of obligations for platforms managing customer and transaction data.
With such a vast regulatory web, achieving compliance can seem overwhelming. Businesses must not only interpret sector-specific mandates but also maintain robust data security practices and keep pace with changing standards.
In the following sections, we’ll break down India’s key data protection laws and demonstrate how ESDS helps enterprises stay compliant, minimize operational strain, and manage data securely across sovereign boundaries.
What is data sovereignty?
Data sovereignty refers to the principle that digital data is subject to the laws and governance of the country in which it is collected, stored and processed. In simple terms, if your organization stores data on servers located in India, that data must comply with Indian laws only, regardless of where your company is headquartered.
Why data sovereignty is important? As organizations go to the cloud, data sovereignty becomes increasingly difficult. Organizations that violate the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe risk fines of up to €20 million. GDPR is applicable not only to EU nations but also to businesses that get data from entities or individuals residing in the EU. This rule has placed significant limitations on companies using a cloud-first strategy and conducting business internationally.
More importantly, some nations have regulations pertaining to data sovereignty that are challenging to understand and much more challenging to follow.
What is data residency?
Data residency refers to the physical or geographic location where an organization’s data is stored and processed, typically determined by the organization’s operational, regulatory, or business requirements. In other words, data residency is about where the data lives, while data sovereignty is about which laws govern it.
Key Takeaways
- Legal jurisdiction is addressed by data sovereignty.
- The geographic location of data storage is reflected in data residency.
- Concerns about data security and privacy are the root of both concepts.
- Some businesses are implementing sovereign clouds as technology, particularly artificial intelligence, advances in order to more readily comply with regional regulations pertaining to data protection, residency, and access.
Data Sovereignty vs. Data Residency: What Sets Them Apart
The words “data residency” and “data sovereignty” are occasionally used synonymously. However, there are three key distinctions between them that might affect an organization’s digital operations, such as choices on data storage and adherence to regulations.
- Scope: –The legal power to control data is known as data sovereignty. For instance, this authority is shared by the federal government and each state in the United States. The actual location of data storage, which establishes which government has sovereignty, is referred to as data residency. Because it is located in both France and the EU, a data center in Marseille is governed by both regulations.
- Focus: – Countries enact laws and rules controlling the handling and storage of data under data sovereignty. For instance, personal information pertaining to racial or ethnic origin, political viewpoints, religious convictions, union participation, genetics, or biometrics is protected under Brazil’s General Data Protection Law. Organizations must abide by local data rules under data residency or risk fines. In 2023, the Irish Data Protection Commission fined IT company Meta €1.2 billion for exporting personal data to the US unlawfully, in accordance with Irish and EU legislation.
- Benefit: – Countries have the right to safeguard the security and privacy of data inside their borders thanks to data sovereignty. In the past, businesses were free to use personal data as they pleased, including selling it to other parties for use in advertising without permission. Businesses may determine whether national laws pertain to data management, including requirements for data protection, access, and usage, by comprehending data residency. It plays a crucial role in determining where data should be stored and indicates that technological and policy modifications are necessary to adhere to local regulations.
Comparison Between Data Sovereignty vs. Data Residency
| Data Sovereignty | Data Residency |
| Governments have the legal authority to control data through data sovereignty. | The physical location of data storage determines which government or regional entity has sovereignty over it. This is known as data residency. |
| One approach to describe how the two ideas vary is as follows: Data sovereignty is a wide legal notion. | However, data residency, which is also a legal notion, delves into the specifics of handling and storing data. |
| Countries adopt laws and rules controlling data management and preservation under data sovereignty; one such law is China’s Personal Information Protection Law. | Under data residency, organizations must comply with local data laws or face penalties. In China, businesses can be fined as much as 50 million yuan per violation. |
| Countries have the right to safeguard the security and privacy of data inside their borders thanks to data sovereignty. | By recognizing data residency, organizations know which national laws apply to data management, including requirements of security, access, and usage. |
| Before going to data sovereignty laws, businesses had few regulations on using personal data, including selling it without approval to third parties. | Today, maintaining up with transforming laws on data privacy and security is a routine part of executing global organization. |
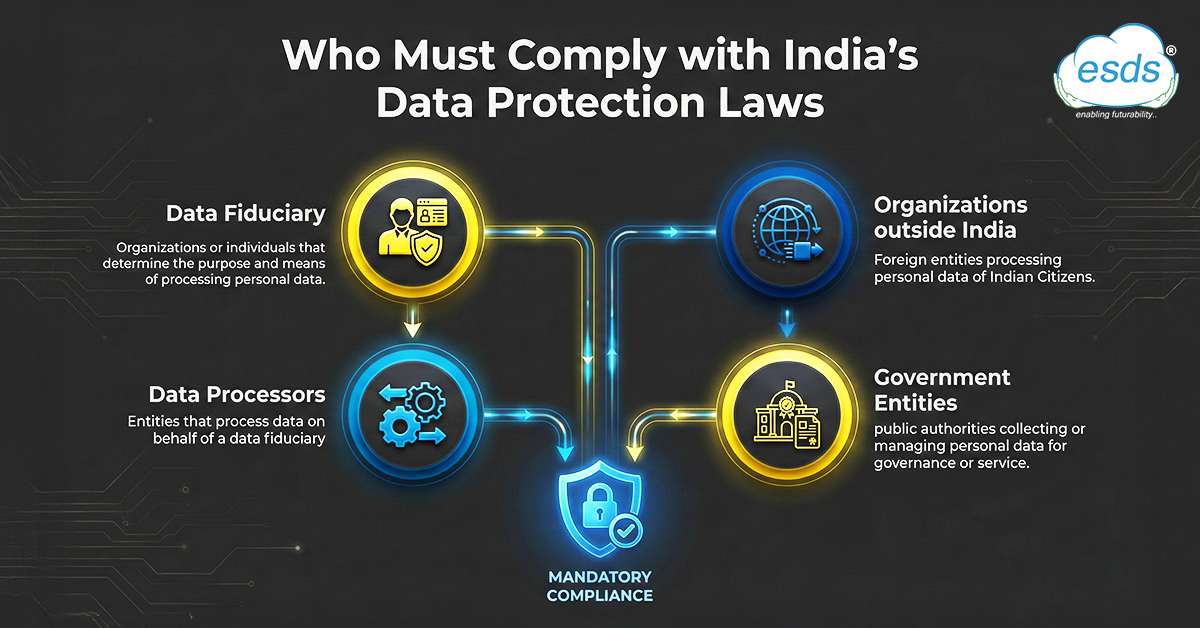
Who Does India’s Data Protection Law Apply To?
With around five key laws covering different sectors of the economy, India has one of the most complex networks of data privacy legislation. Business executives may find it difficult to navigate this complicated legal environment, particularly if they operate in several different industries. A patchwork of compliance duties results from the distinct regulations that apply to each sector.
For instance, the IT industry is governed by two different laws, whereas the telecom industry is governed by the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI). Furthermore, the Indian Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (DPDP Act) regulates any industry where Indian citizens’ personal data is gathered, handled, or disseminated. Furthermore, it is anticipated that the planned National E-Commerce Policy would include even additional regulations for companies that handle customer and transaction data.
Below is the entity that are obligated to comply with all applicable Indian data protection laws: –
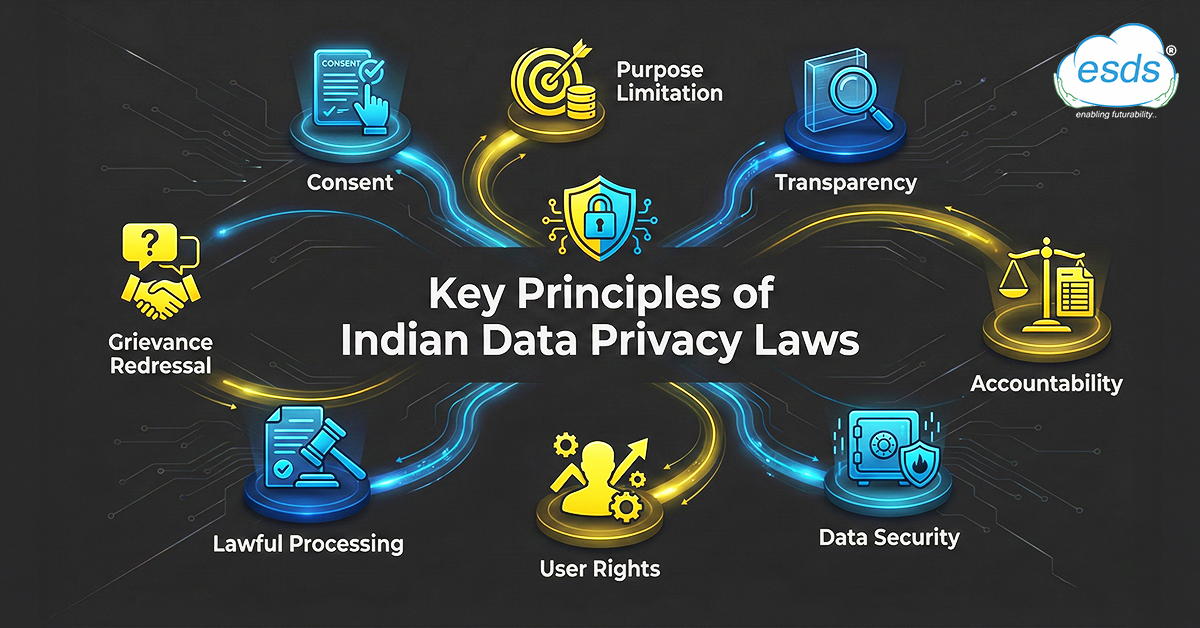
What You Need to Know About Indian Privacy laws?
Below are the highlighted key data privacy policies in India that govern data privacy. They are as follows: –
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 (DPDP Act)
Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDP Act), also referred to as India’s personal data protection bill, is a comprehensive law that regulates the gathering, storing, and processing of personal data. In order to protect personal privacy, it presents important concepts including permission, data reduction, and user rights. Even international organizations that handle the personal data of Indian residents are subject to this rule. The DPDP Act has severe consequences for noncompliance, which emphasizes how crucial it is to follow its rules.
- Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000
The legal foundation for cyber activity in India is the Information Technology Act (IT Act). The IT Act’s Sections 43A and 72A particularly deal with data protection. Provisions for compensating anyone impacted by data breaches brought on by a company’s carelessness are outlined in Section 43A. In order to ensure accountability, Section 72A penalizes anyone who improperly reveal personal information.
- Consumer Protection Act, 2019
Consumer interests are protected by the Consumer Protection Act, which also guards against the improper use of personal information. It gives customers a way to lodge complaints and seek compensation for any harm brought on by unfair business practices or rights violations. Customers are now able to take legal action against companies that violate data privacy regulations thanks to this measure.
- Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) Regulations
Data privacy in the telecom industry is governed by the Telegraph Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI). It includes particular rules to stop telecom corporations from abusing consumer information. These rules guarantee the responsible and secure handling of consumer data, protecting their right to privacy.
Key Principles of Indian Data Privacy Laws
Adopt Indian Data Sovereignty with ESDS Sovereign Cloud
ESDS Sovereign Cloud enables organizations to host data in India while maintaining control, compliance, and security. Built on ESDS’ patented eNlight Cloud technology, it promotes data sovereignty by keeping information under Indian jurisdiction and reducing vulnerability to foreign rules. The platform is designed for government agencies, businesses, and regulated sectors, and it offers scalable infrastructure, controlled security operations, GPU-as-a-Service, and high operational reliability. With Tier III colocation data centers across India, ESDS assists enterprises in meeting localization standards, improving performance, and ensuring business continuity, all in line with India’s goal for safe and self-reliant digital infrastructure.
To simplify this journey, you can explore our detailed guide, 7 Steps to Build a Strong Data Sovereignty Framework — that outlines practical measures for creating a compliant and resilient data environment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is ESDS Sovereign Cloud and how does it support data sovereignty?
ESDS Sovereign Cloud is an India-based platform that ensures data is hosted and governed entirely within Indian jurisdiction, supporting full data residency and compliance.
2. Why is hosting data on foreign cloud platforms risky?
Foreign cloud providers may be subject to their home country’s laws, risking exposure of Indian data to external jurisdictions.
3. Which regulations make sovereign infrastructure essential in India?
Laws like the Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Act, 2023, and emerging data localization policies require storing and processing data within India.
4.How does ESDS provide data control and security?
ESDS gives enterprises full control over encryption keys and access, supported by advanced SOC and SOAR security operations.
5. What services does ESDS Sovereign Cloud offer?
It includes scalable cloud infrastructure, managed security, GPU-as-a-Service, and colocation, powered by ESDS’s patented eNlight platform.
6. What infrastructure supports the ESDS Sovereign Cloud?
ESDS operates Tier III data centers across India, ensuring high uptime, compliance, and business continuity.
- Enlight AIOps: A Unified Framework for AI Operations - March 3, 2026
- How Modern Data Centers Power AI at Scale in 2026 - February 23, 2026
- How To Choose a Cloud GPU Provider In 2026 - January 30, 2026
