From Passwords to Protection – Enhancing Cyber Security via Passwordless Authentication

Stolen passwords are a factor in 81% of breaches, highlighting the critical importance of cyber security. It has long been known that passwords are not secure. They are difficult to recall and simple to lose, making them susceptible to various cyber security threats. They are also the primary target of online fraudsters, underscoring the need for robust cyber security measures.
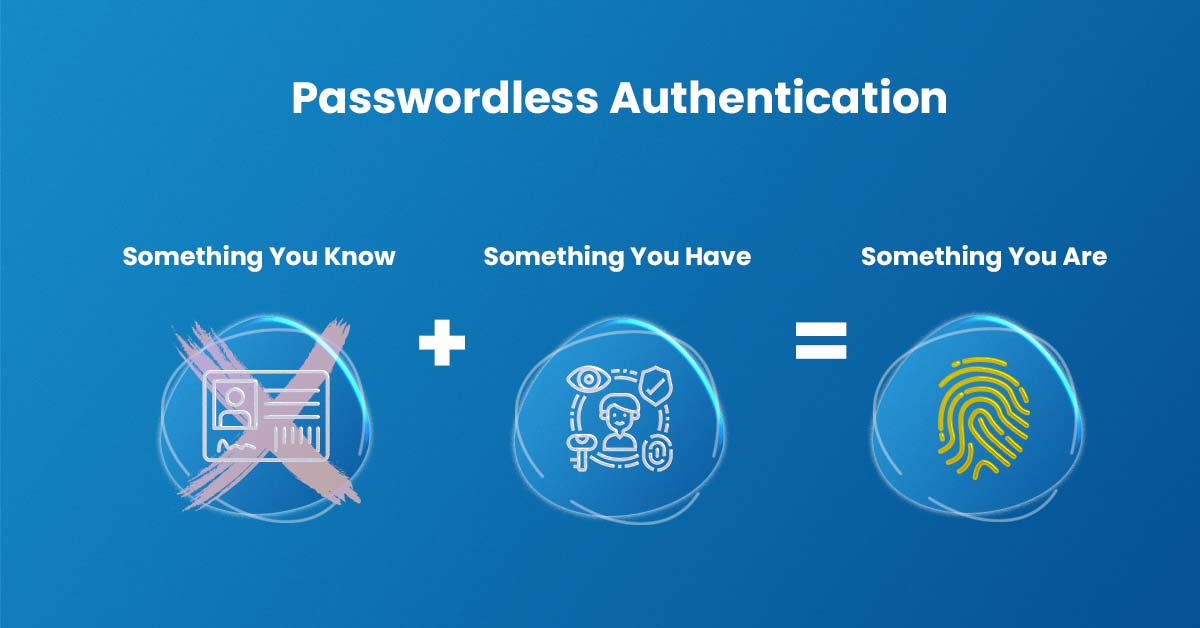
Without the use of a password, passwordless authentication verifies a user’s identity, enhancing cyber security. The usage of biometrics (fingerprint, retina scans) or possession factors (registered smartphones, one-time passwords [OTP], etc.) as opposed to passwords is safer and more resilient against cyber security attacks.
Let’s take a closer look at passwordless authentication and its significance in cyber security.
What Kinds of Authentication Are Passwordless?
There are many methods to accomplish passwordless authentication, all contributing to better cyber security. To name a few:
Biometrics: A person can be uniquely identified by physical characteristics like fingerprints or retinal scans, enhancing cyber security. Behavioral traits like typing and touch screen dynamics also play a role in this secure authentication method.
Aspects of Possession: Authentication by a possession or item that the user is carrying, adding to cyber security. A hardware token, an OTP sent through SMS, or a code produced by a smartphone authenticator app are a few examples.
Magic Links: When a user inputs their email address, the system automatically sends them an email. The email includes a link that, when clicked, gives the user access, improving cyber security.
What Is the Process for Passwordless Authentication?
Passwords are replaced by other, inherently safer authentication variables in passwordless authentication, bolstering cyber security. During password-based authentication, a user-provided password is compared to the database’s entries.
Comparisons may take place in different ways in other passwordless systems. For instance, a system might transmit a one-time passcode through SMS to a user’s mobile device, adding an extra layer of cyber security. The same concepts that govern digital certificates apply to passwordless authentication, utilizing cryptographic key pairs for added cyber security.
Is It Secure to Authenticate Without Password?
Depending on how you define cyber security, passwordless authentication may or may not be secure. If by safe you mean less vulnerable to hacking attacks and more difficult to crack, then yes, passwordless authentication enhances cyber security.
If by safe you mean that it cannot be hacked, then the answer is no. There isn’t an authentication mechanism in existence that can’t be compromised. Even if there isn’t an obvious way to hack it, the most skilled hackers can work their way around its defenses, emphasizing the ongoing importance of cyber security measures.
Having stated that, passwordless methods are intrinsically more secure than passwords, offering enhanced cyber security. For instance, a malicious actor might employ a dictionary attack, which is sometimes regarded as the most basic hacking approach, to compromise a password-based system. In contrast, breaking into a passwordless system necessitates a substantially higher level of hacking expertise and knowledge, contributing to better cyber security.
Passwordless Authentication vs. MFA
Passwords are simply replaced with a more reliable authentication factor in passwordless authentication, contributing to multi-layered cyber security. MFA (multi-factor authentication), on the other hand, uses multiple authentication factors to confirm a user’s identity, further enhancing cyber security.
Passwordless and MFA are occasionally confused for one another or used interchangeably, but they each have their distinct roles in cyber security. That’s because a lot of conventional password-based login systems have begun adopting a passwordless method as their backup authentication mechanism, strengthening cyber security.

How Can Passwordless Authentication Be Enabled?
A method for implementing password-free authentication is as follows, while prioritizing cyber security:
1. Select a mode, considering factors like biometrics and possession for enhanced cyber security.
2. Determine the number of authentication variables to ensure robust cyber security.
3. Purchase necessary hardware/software, which may include biometric scanners or mobile OTP software, for improved cyber security.
4. Begin adding users to your authentication system, ensuring their biometric data or other secure factors are properly integrated for cyber security.
Internally implementing passwordless authentication can be difficult and time-consuming. Many firms choose to outsource their IAM (Identity and Access Management) needs to independent companies, further streamlining the process and ensuring cyber security.
The Future is Password-Free and Cyber Secure
Passwords are still used worldwide, but the increasing frequency of cyberattacks necessitates stronger cyber security measures. With the rise of biometrics and adaptive authentication, cyber security is becoming a top priority for businesses.
Businesses now understand that passwords are the main cause of data breaches, emphasizing the need for enhanced cyber security. When compared to the potential losses from a data breach, the expense of deploying passwordless authentication is negligible.
Combining Passwordless With Adaptive (Behavioral) Authentication for Robust Cyber Security
Despite the advancements in passwordless authentication, it’s important to acknowledge that it’s not foolproof. Hardware tokens, OTPs, and biometrics can all be intercepted, necessitating an adaptive authentication system for comprehensive cyber security.
Adaptive authentication uses machine learning to identify unusual user activity, bolstering cyber security. By analyzing patterns, the system can respond to potential threats appropriately, adding an extra layer of cyber security.
When passwordless and adaptive authentication are used together, your system becomes substantially more resilient. Passwordless factors are more difficult to hack, and adaptive authentication adds an AI-powered layer of cyber security.
Final Reflections on Enhanced Cyber Security
The transition to passwordless access varies for each business, but it’s a journey worth embarking on for improved cyber security. Finding a passwordless authentication partner and championing cyber security within the organization can facilitate this process.
Moreover, businesses can combine passwordless authentication with smart risk management services for even higher levels of cyber security, ensuring a seamless user experience while minimizing security concerns.
In conclusion, the concepts explored here are just the beginning. Passwordless authentication has a bright future, becoming the preferred method for user authentication and contributing to a more secure cyber security landscape.
- 6 Ways AI Reinvents the Security Landscape - January 9, 2024
- Top 6 Current Cybersecurity Trends For 2024 - January 9, 2024
- What Have We Learned from The Recent Cybersecurity Incidents? - January 3, 2024
