Here is everything you need to know about BlockChain
Blockchain has been making headlines lately for the central banks across the world who are exploring possibilities of bringing in the ingenious technology to mainstream financial transactions. Geeks, on social networks and technology forums, are extensively debating the blockchain revolution that perhaps, is inevitable in the near future. What is the buzz all about? Is it just another fad, a bubble that will eventually burst? Or is it here to change the traditional way of digital transactions. Let’s explore if it is as revolutionary as they say.

What is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a new technology developed by Satoshi Nakamoto – a pseudonym of a person or a group, as no one knows anything about it. It is a distributed database or a file – which is stored in multiple computers located at different locations and the database processing is distributed among them. The BlockChain database is a continuously growing list of Blocks- records of financial transactions, bitcoin exchanges, trade contracts, or anything of value between two parties. It was originally developed for maintaining the BitCoin (BTC) transactions but it soon found applications in other areas.
Note: It is a common misconception that blockchain and bitcoins are one and the same thing. However, bitcoins are the only implementation of blockchain technology. So are the other digital currencies.
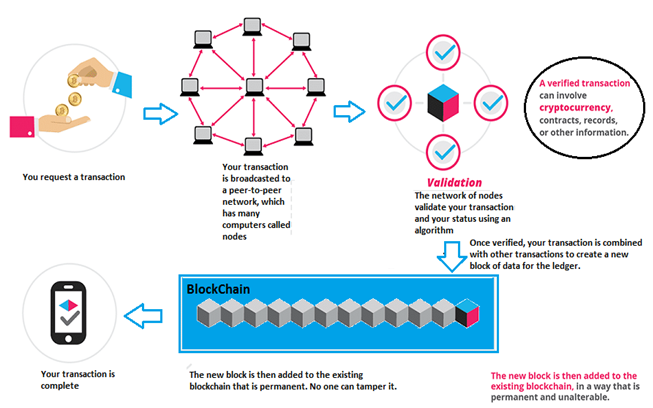
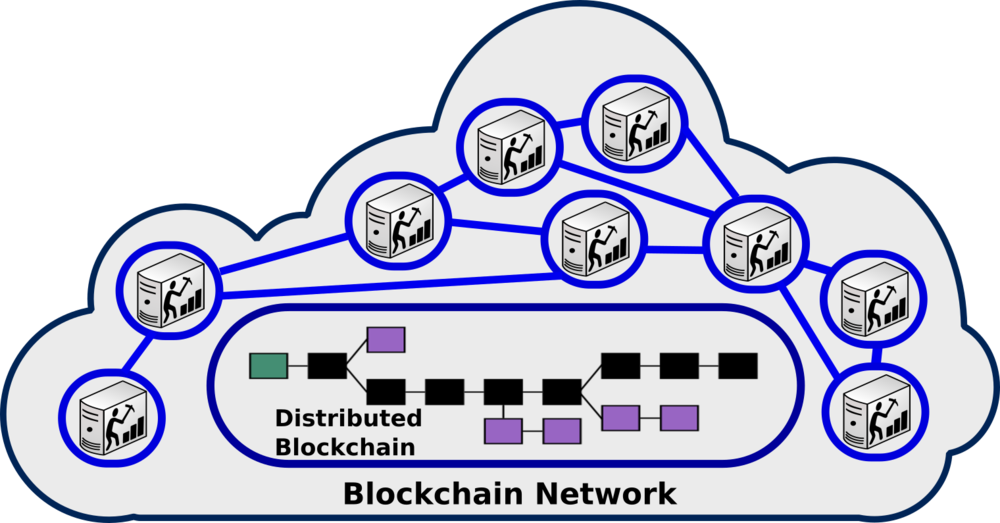
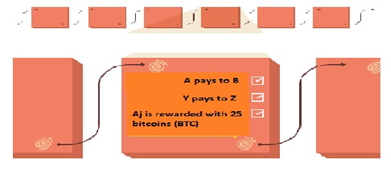
A peer-to-peer (P2P) network which consists of many voluntary participating nodes, validates a transaction and adds it into a block. The block is then appended to a large data structure of the blockchain. Every node is an administrator of the blockchain, and joins the network voluntarily (however, each one has an incentive for participating in the network: the chance of winning Bitcoins). A global network of computers uses blockchain technology to jointly manage the database that records transactions. It is hard to manipulate a record once it is added to a blockchain.
In short, blockchain is like a digital ledger that is distributed over many computers and continuously addresses records like in a queue. Its network is similar to BitTorrent (P2P), wherein the transfer is done between the users rather than a powerful central server.
The following figure illustrates the working of blockchain when you do a transaction.
If anyone can participate in the blockchain network, is it secure?
The blockchain is replicated across all the participating nodes (computers in its network) to ensure that each node has the same list of transaction histories at any time. Therefore, the blockchain eliminates the risks that come with data being held centrally at a location. Its network does not have centralized points of vulnerability that unethical elements (hackers) can exploit.
Blockchain encrypts the blocks that are added to the chain. Encryption here is the combination of public and private keys- public keys being the address of the users on the blockchain network. An address looks like 1K31KZXjcochXpRhjH9g5MxFFTHPi2zEXb. Any transaction between the parties is recorded by their addresses which are difficult to track making the involved parties anonymous (That is why ransom was demanded in bitcoins to stop ransomware attacks).
Each block added in a blockchain has:
- The contents of the block, for example in bitcoin, are the bitcoin transactions and the miner incentive reward.
- A header that contains the data about the block. The header includes some technical information about the block, a reference to the previous block, and a fingerprint (hash) of the data contained in this block.
If anyone wants to meddle with any of the data, they have to regenerate all the fingerprints from that point forwards and the blockchain will look different. This is very unlikely because it is very time-consuming and requires tremendous computing power.
Additions to blockchain are publicly viewable and verified. This makes all the records transparent while unalterable.
If a blockchain continuously grows, how are new records added?
Blockchains use a peer-to-peer model of communication. As there are many nodes validating the record, there are chances of a conflict. Blockchains implement an algorithm to avoid or resolve such conflicts. The algorithm looks for new records every ten minutes and it adds to it to further the chain. Blocks of records in the same timestamp are added as branches to the block of the same timestamp.
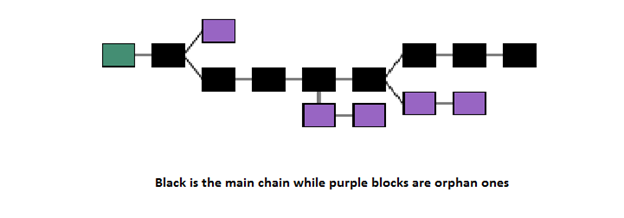 What are the types of blockchain?
What are the types of blockchain?
A blockchain can be implemented by an organization for its business. Blockchain can be of two types:
- Public blockchain.
Anyone is allowed to read and write data. Bitcoin is a public blockchain where the identity of the users is not checked by any authority but they are allowed to add records in the chain. The identity in public blockchain remains anonymous to third parties and therefore it is more vulnerable to malevolent elements who act with impunity.
- Private blockchain.
A Private blockchain is deployed as a proprietary network by an entity like a corporate organization, central banks, etc. Unlike a public blockchain, the participants in a private blockchain are known, trusted, and therefore can be identified.
What are the advantages of blockchain?
Apart from the decentralization and security explained above, some of the other advantages of blockchain are:
- Simplified and faster transaction system. As all the records are merged into a single digital ledger, there is no need for multiple ledgers thus making the maintenance less complicated. Inter-bank transactions can take hours to complete but blockchain can make them faster by executing them instantly.
- Cost reduction. A trusted third party is not needed to facilitate transactions, therefore, the cost of intermediaries is eliminated thereby reducing the transaction costs. Goldman Sachs believes that blockchain technology holds great potential especially to optimize clearing and settlements and could represent global savings of up to $6bn per year.
- Users have complete control over their data and transactions.
- The data involved in blockchain is complete, consistent and verified by multiple peers.
What are the disadvantages of blockchain?
The only cons of blockchain are:
- Performance degradation. Apart from transaction processing, blockchain has to perform other functions like public-private key verification to create consensus among the participating nodes (What if half of the participant nodes approve a transaction but the remaining half do not?) and replicate the chain on every participant node. This slows down a blockchain system.
- Huge computation requirements. Powerful computers are required to validate transactions. According to a study, 450 trillion transactions are processed per second which requires tremendous computing resources.
- Though blockchain offers cost reduction and a faster transaction system and the initial cost to set up an infrastructure for blockchain is very high. Adopting blockchain needs a huge overhaul in the current setup which is not at all easy.
- Blockchain is a very recent technology that is not yet unleashed. There are reservations among organizations and regulatory authorities about its adoption.
What are the potential applications of BlockChain?
- Smart Contracts
Smart contracts help you exchange money, property, shares, or anything of value in a transparent and offer a conflict-free way while avoiding the services of a middleman. Smart contracts use program codes to trigger events automatically responding to other events. For instance, a derivative could be paid when a financial instrument meets a certain benchmark only with the use of blockchain technology and Bitcoin which enables the payout to be automated.
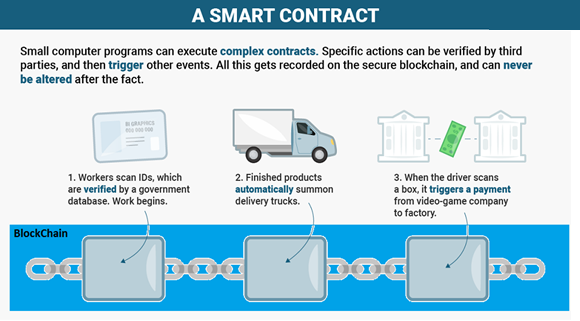
Smart Contracts work on the ‘if-then clause. You can rent a flat through the blockchain environment by paying your rent in cryptocurrency. You get a receipt which is held in a smart contract between you and the owner of the house. The owner gives you the digital entry key which comes to you on a specified date (the date on which the contract will come into effect). Money is automatically refunded to you if the key is not received on time. You get your deposit back when you leave the flat and return the keys. Smart contracts can be effective in case of breach of contracts, property law, credit enforcement, financial services, legal processes, and crowdfunding agreements.
- Direct interactions
Services like Ola, Uber, Swiggy, PayTM, etc. are intermediaries on which you rely for booking a cab, ordering a meal, or recharging your phone. Blockchain can help indirect interaction, the payment between the involved parties.
Smart contracts can make e-governance more efficient and bring transparency in administration. Blockchain could bring full transparency in politics or any other election process. The technology of Ethereum (ETH cryptocurrency) threatens disruptions in the traditional poll process. Boardroom app enables organizational decision-making for the blockchain- which means corporate governance becomes totally transparent and accountable in managing digital assets, equity, or information.
- Tracking/auditing supply chains
Manufacturers make claims about their products being genuine. However, it is often the case when consumers feel cheated as they do not get authentic products. With the transparency offered by blockchain, consumers can track the supply chain of a product (Its origin, Value-added at different stages, etc.). A UK-based startup Provenance leverages the Ethereum blockchain offers to the audit supply chains for many goods.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Sensors, Software, appliances, animals, etc. all are connected to communicate and respond to specific events automatically. Blockchain, Smart Contracts carry out remote management of IoT components making them more efficient and cost-efficient. Ethereum based smart contract is a good example. It redistributes the excess energy generated from electricity grids to neighboring micro-grids. Brooklyn-based Consensys has developed an intelligent grid to automate the monitoring and redistribution of grid energy on similar lines.
- Banking KYC and Preventing Money Laundering
KYC in financial institutions and Anti Money Laundering (AML) has a strong use-case to adopt blockchain. KYC costs could be reduced through cross-institution verification of clients while analyzing it effectively. Startup Polycoin offers a solution to analyze transactions on a blockchain. Those transactions which are identified as suspicious are forwarded to regulatory authorities for review. Creating a private blockchain to carry out financial transactions where all the users have an identity can help the central bank to analyze the transactions and check illicit financial activities.
- Maintaining government records
Government agencies can use blockchain to do all sorts of record keeping. Property titles, entitlements, judicial records, and tax details of the citizens can be maintained in a private blockchain to avoid civil conflicts and frauds. A number of countries like Georgia, Honduras, and Sweden have undertaken blockchain-based land registry projects and many more governments across the world are exploring the possibilities.
- Stock Markets
BlockChain can expedite the stock transfer and settlement process which requires at least 3 working days. A stock trade would happen directly and instantly between buyers and sellers without needing intermediaries like brokers, depositories, and clearinghouses. Top stock and commodities exchanges like the ASX (Australian Securities Exchange), the Deutsche Börse (Frankfurt’s stock exchange) and the JPX (Japan Exchange Group) are prototyping blockchain technology to increase their service delivery.
- Medical
Hospital chains can use a blockchain to keep the medical histories of patients. Treatment of a patient can be started by referring to his medical history. A blockchain can also help insurance companies to settle medical claims.
Private blockchains in enterprise and government agencies can leverage the blockchain. Blockchain, being a concept can be modified to cater to the needs of an organization.
- Apache versus NGINX – Which Open Source Web Server Software you should choose - April 30, 2018
- Understanding OpenStack - April 30, 2018
- Here is everything you need to know about BlockChain - April 17, 2018
Hey It's a nice post I got to know more about block chain and its application, I really appreciate your efforts and this post Thank you
Thank you Ibhaan.